Welcome to the new Traders Laboratory! Please bear with us as we finish the migration over the next few days. If you find any issues, want to leave feedback, get in touch with us, or offer suggestions please post to the Support forum here.
-
Content Count
1193 -
Joined
-
Last visited
Posts posted by Igor
-
-
Currency Convertibility depends on a number of factors, such as the size of the economy and the flexibility of the government's currency policy. Currencies with low convertibility levels are also referred to as illiquid.
-
A Currency Converter enables traders to know the value of a currency relative to its trading counterparts and these numbers can be multiplied based on the number of units that will be traded.
-
While Currency Certificate establish currency values at a fixed rate, the holder is still vulnerable to external shocks in the forex market, as negative price fluctuations will devalue the worth of the note.
-
In a carry trade, investors will borrow in a currency with a low interest rate in order to buy a currency with a higher interest rate. The investor will profit from the difference in these rates and since these profits accumulate over time, carry trades are generally long term positions.
-
Currency Binaries are relatively new in the financial markets and because of this, only the most liquid pairs can be traded in this manner. These trades use directional forecasting, as traders will profit from the direction of an exchange rate rather than the targeting of specific price levels.
-
The Euro is an example of a currency basket and the aim of this type of approach to currency values is meant to limit extreme volatility that can be seen in the various currencies of the region.
-
Currency Arbitrage is relatively rare in the modern trading age, as computer trading has mostly eliminated the ability to simultaneously trade currencies with different brokers at advantageous prices.
-
Currency Appreciation can occur for a number of reasons, such as an increase in interest rates, inflation levels, or economic prospects.This is essentially what occurs when buyers are positive on the prospects of a currency.
-
In general, each country has its own means of monetary transactions, and this is referred to as the national currency. There are exceptions to this, such as the Euro, where more than one country adopts the same monetary unit.
-
Cross-Currency Settlement Risk is a characteristic of the forex markets because of the global nature of each transaction. In many cases, the opposing currency in a forex transaction is not received until that particular market is open for business.
-
Cross Rates make a distinction between the domestic country and two currencies of foreign countries. There are no other differences in these currency pairs, other than the fact that they do not involve the domestic currency.
-
Historically, all foreign exchange transactions required an initial conversion into the US Dollar. Because of this, non Dollar forex pairs continue to be called Cross Pairs.
-
The US Dollar is the world reserve currency and since most global currencies first needed to be converted to the US Dollars before foreign exchange transactions could take place, any non Dollar forex pair is considered to include only cross currencies.
-
The aim of credit netting is to reduce the number of credit checks that need to be conducted. The forex market is arguably the most active market and it is viewed as preferable to reduce the number of credit checks that are needed for leveraged trades.
-
Credit Checking is similar in the forex world as in the rest of the marketplace. Forex is a highly leveraged market and proper credit checks must be conducted to ensure that forex transactions rund smoothly.
-
A Crawling Peg is generally seen when a national government understands that the currency cannot remain fixed but at the same time there is no desire to allow the currency to trade freely on the open markets.
-
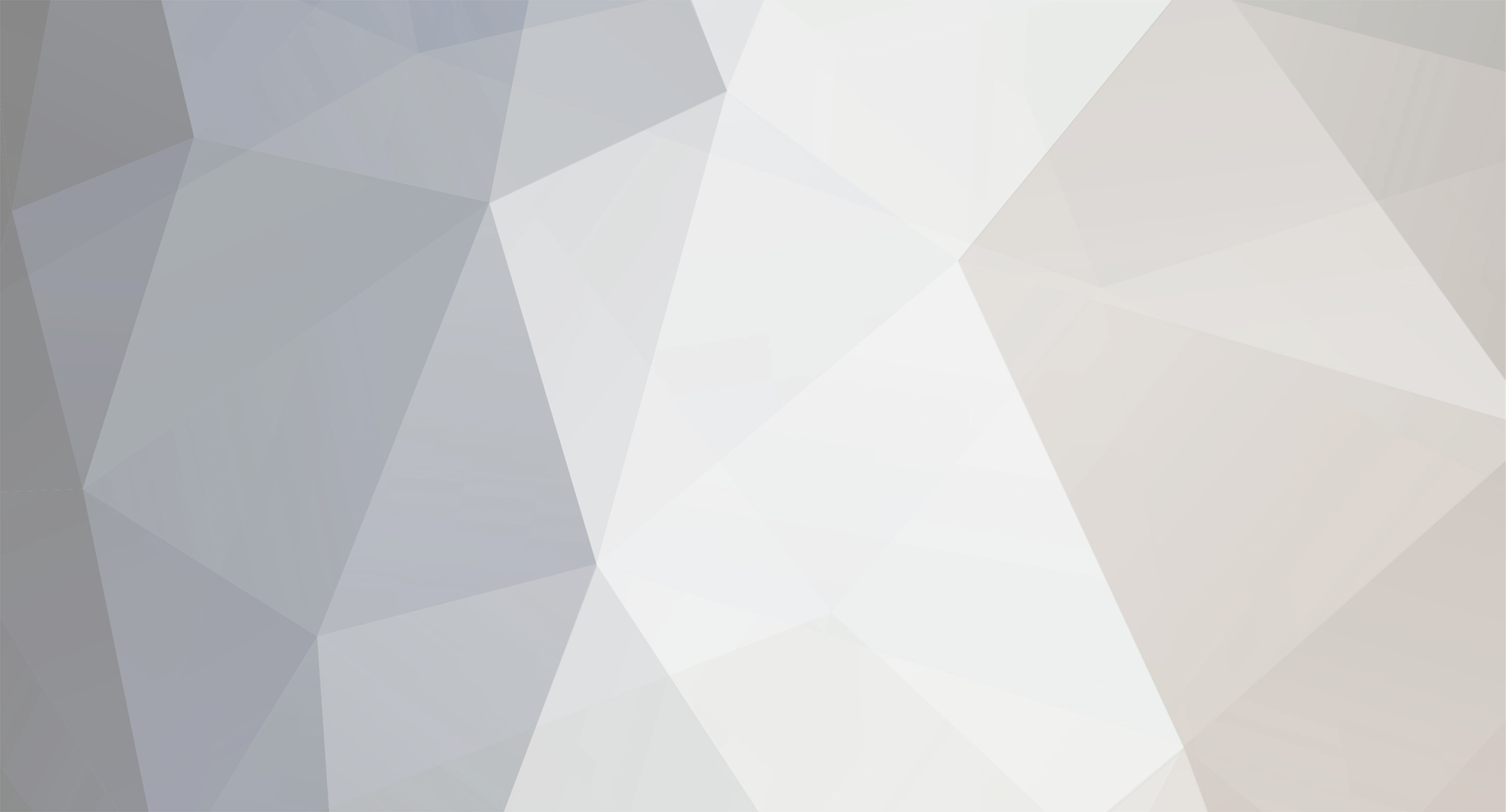
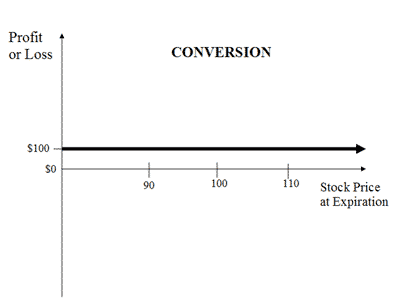
Traders who implement a conversion strategy are taking advantage of overpriced assets by instantly liquidating (arbitraging) them to fair market value. The technique involves selling and purchasing a put and a call option, at-the-money, while going long on the underlying asset. Traders can earn a small, risk-free profit when converting options, as long as the option's strike prices exceed the prices of the associated underlying asset.
Moneyness Review for Puts and Calls
Call Options:
In-The-Money (ITM) = Strike price (less than) Market Price
Out-of-The Money (OTM) = Strike price (more than) Market Price
Put Options:
In-The-Money (ITM) = Strike Price (more than) Market Price
Out-of-The Money (OTM) = Strike Price (less than) Market Price
Both Put and Call Options
At-The-Money (ATM) Strike Price (equals) Market Price
How to Carry Out A Conversion Strategy
Disney stock is worth $100 (market price) in June.
1) Trader buys 100 shares of Disney stock.
2) Trader buys the put option: DISJul100($3)
- 100 shares of Disney stock
- Strike Price $100, at-the-money (ATM), expiring in 30 days
- Premium Cost of $3
3) Trader sell the call option: DISJul100($4)
- 100 shares of Disney stock
- Strike Price $100, at-the-money (ATM), expiring in 30 days
- Premium Cost of $4
4) Trader pays $9900 to enter the conversion. [$9900 (paid for shares) + $400 (received from call) - $300 (paid for put)]
Total cost to enter the market: $9900
Result one: Disney stock rises (rallies) to $110 in July.
a) The put option purchased expires worthless. (OTM)
b) The call option sold expires ITM.
c) The investor who bought the trader's call option exercises his or her right to buy 100 shares at $100.
d) The trader uses the 100 shares to cover the assignment and receives $10000 from the buyer.
e) Trader gains a total of $100 after the subtracting the cost to enter the market from the funds collected from the call option. [$10000 (received from call buyer) - $9900 (cost to enter market)]
Result two: Disney stock falls to $90 in July.
a) The call option sold expires worthless. (OTM)
b) The put option purchased expires ITM.
c) The trader exercises his or her right to sell 100 shares at $100, receiving $10000 from the buyer for the long shares purchased when entering the trade.
d) The trader's profit totals $100 after the subtracting the cost to enter the market from the funds collected from the put option. [$10000 (received from put seller) - $9900 (cost to enter market)]
Calculating The Risk-Free Profit In A Conversion
Investors earn instant profits when correctly entering a conversion trade. Market conditions will not matter at the time of expiration, as the synthetic long position covers losses and cancels gains on the long trade. In order to achieve instant profits, the options' strike prices must exceed the difference in the price of the underlying asset less the cost to enter the market. [$100 = $100 (options' strike prices) - $100 (cost to enter market) + $100 (asset price)]
Advantages and Disadvantages of Implementing a Conversion :
Pluses: The upside to this type of strategy is that the investor will always make a small profit in any market situation, risk-free. The trader is just converting the overpriced options to fair market value.
Minuses: There is no downside in carrying out a reversal strategy, since it risk-free. However, traders must be able to recognize overpriced options of which values are higher than their associated underlying asset.
-
Traders who implement a reversal strategy are taking advantage of under priced assets by instantly liquidating (arbitraging) them to fair market value. The technique involves selling and purchasing a put and a call option, at-the-money, while short selling the underlying asset. Traders can earn a small, risk-free profit when using a reversal strategy, as long as the two under priced option's values are lower than their associated underlying asset.
Moneyness Review for Puts and Calls
Call Options:
In-The-Money (ITM) = Strike price (less than) Market Price
Out-of-The Money (OTM) = Strike price (more than) Market Price
Put Options:
In-The-Money (ITM) = Strike Price (more than) Market Price
Out-of-The Money (OTM) = Strike Price (less than) Market Price
Both Put and Call Options
At-The-Money (ATM) Strike Price (equals) Market Price
How to Carry Out A Reversal Strategy
Disney stock is worth $100 (market price) in June.
1) Trader short sells 100 shares of Disney stock.
2) Trader sells the put option: DISJul100($4)
- 100 shares of Disney stock
- Strike Price $100, at-the-money (ATM), expiring in 30 days
- Premium Cost of $4
3) Trader buys the call option: DISJul100($3)
- 100 shares of Disney stock
- Strike Price $100, at-the-money (ATM), expiring in 30 days
- Premium Cost of $3
4) Trader receives a $10100 credit when entering the market. [$10000 (received from short sale) + $400 (received from put) - $300 (paid for call)]
Total cost to enter the market: -$10100
Result one: Disney stock rises (rallies) to $110 in July
a) The put option sold expires worthless. (OTM)
b) The call option purchased expires ITM.
c) The trader exercises his or her right to buy 100 shares at $100, paying 10000 to the seller.
d) The trader uses the 100 shares to cover the short sale.
e) Trader gains a total of $100 after keeping the remainder of the credit earned when entering the market. [$10100 (credit) - $10000 (paid for shares]
Result two: Disney stock falls to $90 in July.
a) The call option purchased expires worthless. (OTM)
b) The put option sold expires ITM.
c) The investor who bought the trader's put option exercises his or her right to sell 100 shares at $100. The trader pays $10000 to the buyer, and receives 100 Disney shares.
d) The trader uses the 100 shares to cover the short sale.
e) The trader makes a total profit of $100 after keeping the remainder of the credit earned when entering the market. [$10100 (credit) - $10000 (paid to cover put)]
Calculating The Risk Free Profit In A Reversal Strategy
Investors earn instant profits when correctly entering a reversal trade. Market conditions will not matter at the time of expiration, as the synthetic long stock position covers losses and cancels gains on the short sale. In order to achieve instant profits, the price of the underlying asset must exceed the difference in premiums collected less the options' strike prices. [$100 = $100 (asset price) + $100 (premium credit) - $100 (options' strike prices)]
Advantages and Disadvantages of Implementing a Reversal Strategy:
Pluses: The upside to this type of strategy is that the investor will always make a small profit in any market situation, risk-free. The trader is just arbitraging the under priced options to fair market value.
Minuses: There is no downside in carrying out a reversal strategy, since it risk-free. However, traders must be able to recognize under priced options of which values are lower than their associated underlying asset.
-
Forex traders often look for market conditions which out out of equilibrium, for example interest rates are high in value but the spot rate is low. This conditions generally present attractive trading opportunities but when there is Covered Interest Rate Parity, this type of opportunity does not exist.
-
Traders are often instructed to “cover on a approach” when short positions are taken and prices approach a significant area of support. Excessive declines might indicate that prices are ready to reverse upwardly, and thus, sell positions should be closed.
-
Traders are often instructed to “cover on a bounce” when short positions are taken and prices bounce out of a significant area of support. This bounce might indicate that prices are ready to reverse upwardly, and thus, sell positions should be closed.
-
Country risks can involve a wide variety of things but will always be the source of negative economic growth for at least one aspect of a country's economic. Country Risks include things like high inflation levels, poor GDP growth, or excessive debt.
-
Counter currencies are generally seen as the more liquid currency in a given forex pair. This can be seen in many examples, such as the GBP/USD or AUD/JPY and the counter currency provides a measure for the value of the first currency listed. For example, in the EUR/USD we can see how number of Euros it takes to purchase 1 US Dollar.
-
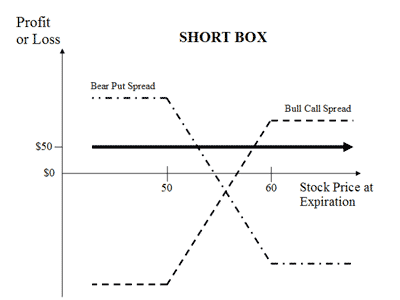
Traders who implement a short box strategy are taking advantage of overpriced assets by instantly liquidating (arbitraging) them to fair market value. The technique involves selling both a bull call and bear put spread at the same time, using options with parallel strike prices and expirations. Traders can earn risk-free profit, as long as the credit received when entering the market exceeds the expiration value of the box.
Moneyness Review for Puts and Calls
Call Options:
In-The-Money (ITM) = Strike price (less than) Market Price
Out-of-The Money (OTM) = Strike price (more than) Market Price
Put Options:
In-The-Money (ITM) = Strike Price (more than) Market Price
Out-of-The Money (OTM) = Strike Price (less than) Market Price
Both Put and Call Options
At-The-Money (ATM) Strike Price (equals) Market Price
How To Set Up A Short Box Strategy
Disney stock is worth $55 (market price) in July.
Selling the Bull Call Spread
1) The trader writes (sells) a call option: DISAug50($7)
- 100 shares of Disney stock
- Strike Price $50 (ITM), expiring in 30 days
- Premium Cost of $7
2) The trader buys a call option: DISAug60($1.50)
- 100 shares of Disney stock
- Strike Price $60 (OTM), expiring in 30 days
- Premium Cost of $1.50
3) The trader receives a credit of $550 when entering the bull call spread. [$700 (received from call sale) - $150 (paid for call purchase)]
Selling the Bear Put Spread
1) Trader writes (sells) a put option: DISAug60($7)
- 100 shares of Disney stock
- Strike Price $60 (ITM), expiring in 30 days
- Premium Cost of $7
2) Trader buys a put option: DISAug50($2)
- 100 shares of Disney stock
- Strike Price $50 (OTM), expiring in 30 days
- Premium Cost of $2
3) The trader receives a credit of $500 when entering the bear put spread. [$700 (received from put sale) - $200 (paid for put purchase)]
Total (Short Box) credit when entering the market $1050: [$550 (credit from bull spread) + $500 (credit from bear spread)]
Computing Expiration Value
To earn risk-free profit, the credit received when entering the market must exceed the expiration value of the box. The expiration value is simply the difference between the higher and lower strike prices, multiplied by 100. This example's box spread expiration value is $1000 [$1000= $60 (high) - $50 (low) X 100], which is lower than the $1050 credit when entering the market.
Result one: Disney stays at $55 (ATM) in August.
a) Both the put and call options purchased expire worthless (OTM).
b) The put option sold is ITM The buyer exercises his or her right to sell the trader 100 shares at $60. The trader pays $6000 to the seller.
c) The call option sold is ITM. The buyer exercises his or her right to buy shares at $50 from the trader, who sells the 100 shares and receives $5000 from the buyer.
d) The trader's profit is $50 after adding the credit received when entering the market from the loss. [$50 = $5000 (received from call buyer) - $6000 (paid to put buyer) + $1050 (credit)]
Result two: Disney rallies to $60 in August.
a) Both the put and call options purchased and the put option sold expire worthless (OTM).
b) The call option sold is ITM.
c) The trader buys 100 Disney shares in the open market to cover the sale, paying $6000.
d) The buyer exercises his or her right to buy shares at $50 from the trader, who sells the 100 shares and receives $5000 from the buyer.
e) The trader's profit is $50 after adding the credit received when entering the market from the loss. [$50 = $5000 (received from call buyer) - $6000 (paid for shares) + $1050 (credit)]
Result three: Disney falls (crashes) to $50 in August.
a) Both the put and call options purchased and the call option sold expire worthless (OTM).
b) The put option sold is ITM.
c) The buyer exercises his or her right to sell the trader 100 shares at $60. The trader pays $6000 to the seller.
d) The trader sells 100 Disney shares in the open market at $50 and receives $5000.
e) The trader's profit is $50 after adding the credit received when entering the market from the loss. [$50 = $5000 (received from put buyer) - $6000 (share sale) + $1050 (credit)]
Advantages and Disadvantages of Implementing a Small Box Strategy:
Pluses: The upside to this type of strategy is that the investor will always make a small profit in any market situation, risk-free. The trader is just arbitraging the overpriced options to fair market value.
Minuses: There is no downside in carrying out a short strategy, since it risk-free. However, traders must be able to quickly recognize options with overpriced expiration values.



Currency Day Trading System Definition
in Trading Dictionary
Posted
Currency Day Trading Systems differ in many ways, with some traders focusing on fundamental economic factors and other using charting analysis as the basis for positions.